Aug 2, 2023Equilibrium is a point of stability where there is no economic incentive to change. A price-taking perfectly competitive firm may therefore lose profit upon converging upon the equilibrium price. The overall point is the perfectly competitive market converges on a point where all profit have been completely exhausted.
Long-Run Equilibrium under Perfect Competition – II
To find TR, multiply the price of the goods by the quantity of goods sold: TR = pq Average revenue (AR) is the average amount of money that the firm gets per unit of goods. This is equal to p, the market price, since the firm cannot decide how much people will pay for its goods. AR = TR/q AR = p

Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
A Decrease in Demand. Panel (b) of Figure 3.10 “Changes in Demand and Supply” shows that a decrease in demand shifts the demand curve to the left. The equilibrium price falls to $5 per pound. As the price falls to the new equilibrium level, the quantity supplied decreases to 20 million pounds of coffee per month.
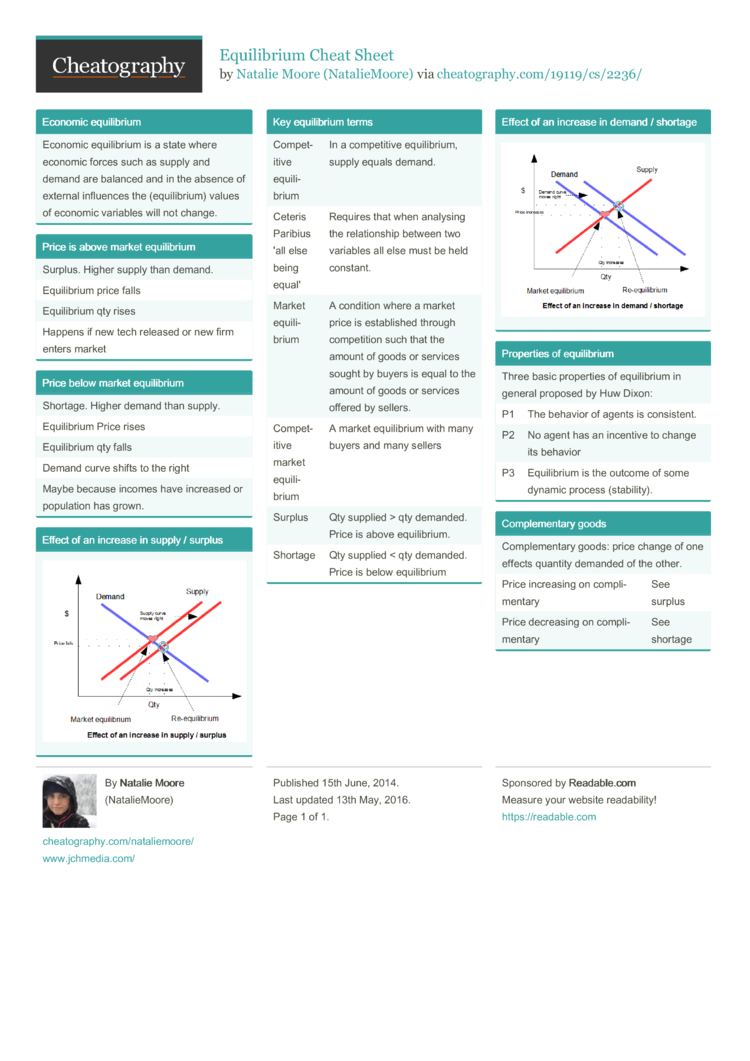
Source Image: cheatography.com
Download Image
Economic equilibrium: Achieving Normal Profit in a Competitive Market – FasterCapital Competitive equilibrium (also called: Walrasian equilibrium) is a concept of economic equilibrium, introduced by Kenneth Arrow and Gérard Debreu in 1951, appropriate for the analysis of commodity markets with flexible prices and many traders, and serving as the benchmark of efficiency in economic analysis. It relies crucially on the assumption of a competitive environment where each trader

Source Image: m.youtube.com
Download Image
If Equilibrium Is Achieved In A Competitive Market
Competitive equilibrium (also called: Walrasian equilibrium) is a concept of economic equilibrium, introduced by Kenneth Arrow and Gérard Debreu in 1951, appropriate for the analysis of commodity markets with flexible prices and many traders, and serving as the benchmark of efficiency in economic analysis. It relies crucially on the assumption of a competitive environment where each trader Longrun equilibrium in perfectly competitive markets meets two important conditions: allocative efficiency and productive efficiency. These two conditions have important implications. First, resources are allocated to their best alternative use. Second, they provide the maximum satisfaction attainable by society.
Practice Problem: Firm and Market Equilibrium in Perfect Competition – YouTube
Key points. There is a four-step process that allows us to predict how an event will affect the equilibrium price and quantity using the supply and demand framework. Step one: draw a market model (a supply curve and a demand curve) representing the situation before the economic event took place. Long Run Equilibrium of Competitive Firm and Industry

Source Image: toppr.com
Download Image
Equilibrium of Firm Under Perfect Competition | PPT Key points. There is a four-step process that allows us to predict how an event will affect the equilibrium price and quantity using the supply and demand framework. Step one: draw a market model (a supply curve and a demand curve) representing the situation before the economic event took place.

Source Image: slideshare.net
Download Image
Long-Run Equilibrium under Perfect Competition – II Aug 2, 2023Equilibrium is a point of stability where there is no economic incentive to change. A price-taking perfectly competitive firm may therefore lose profit upon converging upon the equilibrium price. The overall point is the perfectly competitive market converges on a point where all profit have been completely exhausted.

Source Image: toppr.com
Download Image
Economic equilibrium: Achieving Normal Profit in a Competitive Market – FasterCapital A Decrease in Demand. Panel (b) of Figure 3.10 “Changes in Demand and Supply” shows that a decrease in demand shifts the demand curve to the left. The equilibrium price falls to $5 per pound. As the price falls to the new equilibrium level, the quantity supplied decreases to 20 million pounds of coffee per month.

Source Image: fastercapital.com
Download Image
Equilibrium of the Firm and the Industry in Long-Run 5 December 2019 by Tejvan Pettinger Definition of market equilibrium – A situation where for a particular good supply = demand. When the market is in equilibrium, there is no tendency for prices to change. We say the market-clearing price has been achieved. A market occurs where buyers and sellers meet to exchange money for goods.
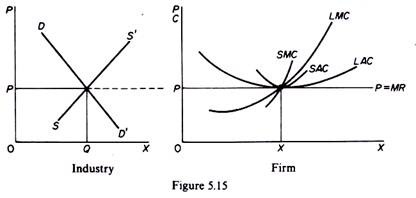
Source Image: economicsdiscussion.net
Download Image
Short Run & Long Run Equilibrium Under Perfect Competition – ppt download Competitive equilibrium (also called: Walrasian equilibrium) is a concept of economic equilibrium, introduced by Kenneth Arrow and Gérard Debreu in 1951, appropriate for the analysis of commodity markets with flexible prices and many traders, and serving as the benchmark of efficiency in economic analysis. It relies crucially on the assumption of a competitive environment where each trader

Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
1.5.2 Perfect Competition Unit Overview – ppt download Longrun equilibrium in perfectly competitive markets meets two important conditions: allocative efficiency and productive efficiency. These two conditions have important implications. First, resources are allocated to their best alternative use. Second, they provide the maximum satisfaction attainable by society.
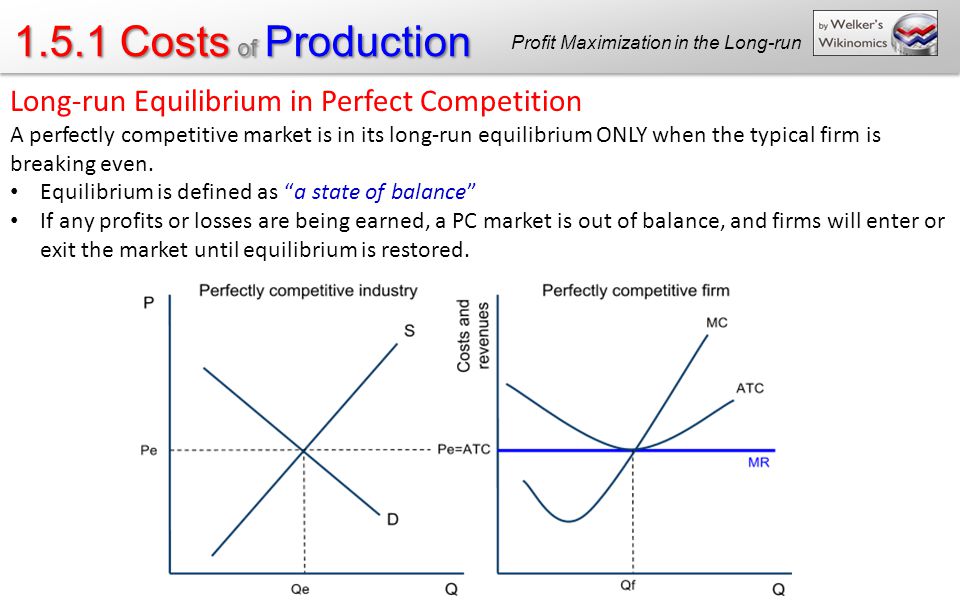
Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
Equilibrium of Firm Under Perfect Competition | PPT
1.5.2 Perfect Competition Unit Overview – ppt download To find TR, multiply the price of the goods by the quantity of goods sold: TR = pq Average revenue (AR) is the average amount of money that the firm gets per unit of goods. This is equal to p, the market price, since the firm cannot decide how much people will pay for its goods. AR = TR/q AR = p
Economic equilibrium: Achieving Normal Profit in a Competitive Market – FasterCapital Short Run & Long Run Equilibrium Under Perfect Competition – ppt download 5 December 2019 by Tejvan Pettinger Definition of market equilibrium – A situation where for a particular good supply = demand. When the market is in equilibrium, there is no tendency for prices to change. We say the market-clearing price has been achieved. A market occurs where buyers and sellers meet to exchange money for goods.