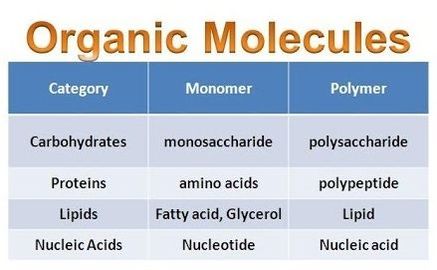
For example, a carbohydrate is a macromolecule that is classified as a polymer because it is made up of repeating monosaccharides, but a fat (lipid) is a macromolecule that cannot be further classified because if you look under the ‘monomers’ column, it is built up by more than one monomer. Hope this helped! 2 comments ( 111 votes) Show more
Large biological molecules and their types discussed | Britannica
May 27, 2023Threose It is also 4 carbon monomer similar to erythrose in structure with a small variation. Five-carbon carbohydrate monomers Ribose sugar It is a 5-carbon monomer. A pentose sugar with many isomers. It is found widely in the Coenzymes, ATP, NADH, nucleic acids of living organisms.
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
Jan 2, 2024What does the word carbohydrate mean? How are carbohydrates classified?
Source Image: mrgscience.com
Download Image
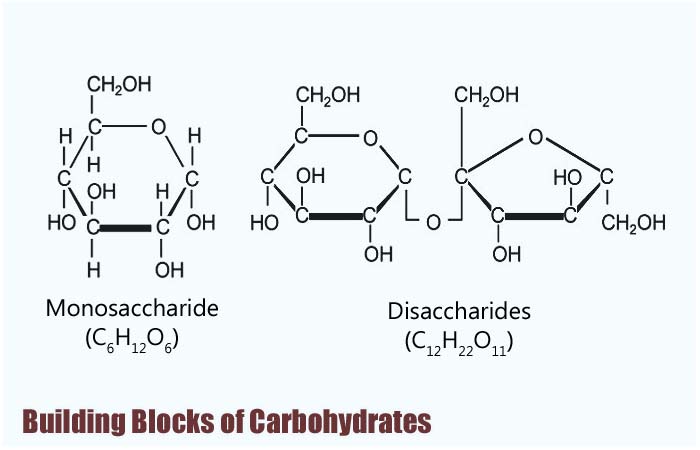
A Green and Sustainable Route to Carbohydrate Vinyl Ethers for Accessing Bioinspired Materials with a Unique Microspherical Morphology – Rodygin – 2018 – ChemSusChem – Wiley Online Library Molecular Structures. Carbohydrates can be represented by the stoichiometric formula (CH 2 O) n, where n is the number of carbons in the molecule. In other words, the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen is 1:2:1 in carbohydrate molecules. This formula also explains the origin of the term “carbohydrate“: the components are carbon (“carbo
Source Image: bioexplorer.net
Download Image
What Are The Monomers Of Carbohydrates Called
Molecular Structures. Carbohydrates can be represented by the stoichiometric formula (CH 2 O) n, where n is the number of carbons in the molecule. In other words, the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen is 1:2:1 in carbohydrate molecules. This formula also explains the origin of the term “carbohydrate“: the components are carbon (“carbo In Summary: Comparing Biological Macromolecules. Proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. Macromolecules are made up of single units known as monomers that are joined by covalent bonds to form
Building Blocks of Carbohydrates | Types, Properties & Functions
3: Biological Macromolecules 3.1: Carbohydrates – Carbohydrate Molecules What Are Monomers Of Carbohydrates? – Database Football

Source Image: databasefootball.com
Download Image
Molecules of Life – Honors Biology 3: Biological Macromolecules 3.1: Carbohydrates – Carbohydrate Molecules

Source Image: frhonorsbiologybeno.weebly.com
Download Image
Large biological molecules and their types discussed | Britannica For example, a carbohydrate is a macromolecule that is classified as a polymer because it is made up of repeating monosaccharides, but a fat (lipid) is a macromolecule that cannot be further classified because if you look under the ‘monomers’ column, it is built up by more than one monomer. Hope this helped! 2 comments ( 111 votes) Show more

Source Image: britannica.com
Download Image
A Green and Sustainable Route to Carbohydrate Vinyl Ethers for Accessing Bioinspired Materials with a Unique Microspherical Morphology – Rodygin – 2018 – ChemSusChem – Wiley Online Library Jan 2, 2024What does the word carbohydrate mean? How are carbohydrates classified?

Source Image: chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Download Image
Monomer Definition, Types & Examples – Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com Carbohydrates provide energy to the body, particularly through glucose, a simple sugar that is a component of starch and an ingredient in many staple foods. … (Figure 4). Glycosidic bonds (also called glycosidic linkages) can be of the alpha or the beta type. Figure 4. Sucrose is formed when a monomer of glucose and a monomer of fructose are

Source Image: study.com
Download Image
2+ Thousand Carbohydrate Biological Molecule Royalty-Free Images, Stock Photos & Pictures | Shutterstock Molecular Structures. Carbohydrates can be represented by the stoichiometric formula (CH 2 O) n, where n is the number of carbons in the molecule. In other words, the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen is 1:2:1 in carbohydrate molecules. This formula also explains the origin of the term “carbohydrate“: the components are carbon (“carbo

Source Image: shutterstock.com
Download Image
What Are Monomers Of Carbohydrates? – Database Football In Summary: Comparing Biological Macromolecules. Proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. Macromolecules are made up of single units known as monomers that are joined by covalent bonds to form

Source Image: databasefootball.com
Download Image
Molecules of Life – Honors Biology
What Are Monomers Of Carbohydrates? – Database Football May 27, 2023Threose It is also 4 carbon monomer similar to erythrose in structure with a small variation. Five-carbon carbohydrate monomers Ribose sugar It is a 5-carbon monomer. A pentose sugar with many isomers. It is found widely in the Coenzymes, ATP, NADH, nucleic acids of living organisms.
A Green and Sustainable Route to Carbohydrate Vinyl Ethers for Accessing Bioinspired Materials with a Unique Microspherical Morphology – Rodygin – 2018 – ChemSusChem – Wiley Online Library 2+ Thousand Carbohydrate Biological Molecule Royalty-Free Images, Stock Photos & Pictures | Shutterstock Carbohydrates provide energy to the body, particularly through glucose, a simple sugar that is a component of starch and an ingredient in many staple foods. … (Figure 4). Glycosidic bonds (also called glycosidic linkages) can be of the alpha or the beta type. Figure 4. Sucrose is formed when a monomer of glucose and a monomer of fructose are